Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver, and it can be caused by various factors, including viral infections. The most common types are Hepatitis A, B, and C, each with distinct transmission modes, symptoms, and treatments. Early diagnosis and effective management are key to preventing complications such as liver damage, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
Causes of Hepatitis A, B, C
- Hepatitis A (HAV): Caused by the Hepatitis A virus, primarily transmitted through contaminated food or water and close personal contact.
- Hepatitis B (HBV): Caused by the Hepatitis B virus, transmitted through infected blood, sexual contact, or from mother to child during childbirth.
- Hepatitis C (HCV): Caused by the Hepatitis C virus, spread primarily through blood-to-blood contact, such as sharing needles or unsafe medical practices.
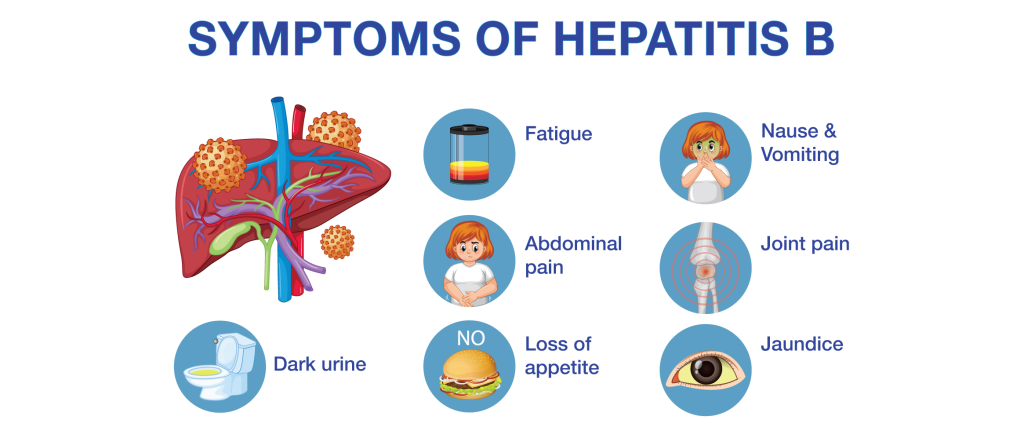
Indications of Hepatitis A, B, C
Early signs and indications include:
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
- Dark urine and pale stools.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort, especially around the liver.
Symptoms of Hepatitis A, B, C
- Hepatitis A:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Fever and chills.
- Temporary symptoms lasting a few weeks to months.
- Hepatitis B:
- Acute phase symptoms similar to Hepatitis A.
- Chronic HBV may lead to liver scarring or cancer over time.
- Hepatitis C:
- Often asymptomatic in early stages.
- Progression may cause chronic liver inflammation, cirrhosis, and cancer.
Prevention Strategies of Hepatitis A, B, C
- Vaccination:
- Safe and effective vaccines are available for HAV and HBV.
- Hygiene Practices:
- Regular handwashing to prevent HAV transmission.
- Safe Practices:
- Avoid sharing needles and ensure safe blood transfusions for HBV and HCV prevention.
- Use condoms to reduce the risk of HBV transmission.
- Screening and Testing:
- Regular testing for high-risk individuals to detect HBV and HCV early.
- Travel Precautions:
- Get vaccinated before traveling to areas with high HAV prevalence.
Myths and Facts About Hepatitis A, B, C

- Myth: Only drug users are at risk of Hepatitis C. Fact: While sharing needles is a risk, unsafe medical practices can also transmit HCV.
- Myth: Hepatitis A is not serious. Fact: Severe cases can lead to acute liver failure, especially in older adults.
- Myth: Hepatitis B is always sexually transmitted. Fact: HBV can also be spread through blood and childbirth.
- Myth: There is no cure for Hepatitis C. Fact: Modern antiviral treatments can cure over 95% of HCV infections.
Treatments and Therapy
Medication-Based Treatments
- Hepatitis A:
- Supportive care; the infection usually resolves on its own.
- Hepatitis B:
- Antiviral medications (e.g., tenofovir, entecavir) to manage chronic HBV.
- Hepatitis C:
- Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) that offer high cure rates.
Surgical Treatments
- Liver transplant may be necessary for individuals with end-stage liver disease caused by chronic HBV or HCV.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
- Recommended for patients recovering from advanced liver disease or transplants.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Interventions
- Avoid alcohol to reduce liver stress.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients to support liver health.
Alternative and Complementary Medicine
- Herbal remedies like milk thistle may support liver health but should complement, not replace, medical treatment.
Psychotherapy and Counseling
- Helps patients cope with the emotional burden of chronic illness.
- Support groups for those living with Hepatitis B or C.
Immunizations and Vaccines
- Vaccines for HAV and HBV are essential, especially for high-risk groups.
Stem Cell Therapy
- Research is ongoing; stem cell therapy may offer future solutions for liver regeneration.
Gene Therapy
- Experimental treatments targeting viral genes show promise but are not yet widely available.
Top 20 FAQ on Hepatitis A, B, C

1. What is the difference between Hepatitis A, B, and C?
- Hepatitis A is transmitted through contaminated food or water. Hepatitis B is spread through blood, sexual contact, or childbirth, and Hepatitis C is primarily spread through blood-to-blood contact.
2. Can Hepatitis A resolve on its own?
- Yes, most cases of Hepatitis A resolve without treatment, but rest and supportive care are essential.
3. Is Hepatitis B contagious?
- Yes, it is highly contagious and can spread through blood, sexual contact, and from mother to child during childbirth.
4. What are the early symptoms of Hepatitis C?
- Many people with Hepatitis C have no symptoms initially, but fatigue, fever, and mild abdominal pain may occur.
5. How is Hepatitis diagnosed?
- Diagnosis is made through blood tests to detect viral markers and liver function tests.
6. Are vaccines available for all types of Hepatitis?
- Vaccines are available for Hepatitis A and B but not for Hepatitis C.
7. What are the long-term effects of Hepatitis B?
- Chronic Hepatitis B can lead to liver cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer.
8. Can Hepatitis C be cured?
- Yes, modern antiviral medications can cure over 95% of Hepatitis C cases.
9. How can Hepatitis A be prevented?
- Vaccination, good hygiene, and safe food and water practices are effective preventive measures.
10. Can Hepatitis B resolve without treatment?
- Acute Hepatitis B often resolves on its own, but chronic infections require medical treatment.
11. What foods should be avoided with Hepatitis?
- Fatty, processed, and sugary foods should be avoided to reduce liver strain.
12. Who is most at risk for Hepatitis B?
- Healthcare workers, people with multiple sexual partners, and newborns of infected mothers are at higher risk.
13. Can children contract Hepatitis C?
- Yes, though it is rare, children can contract Hepatitis C, often through mother-to-child transmission during birth.
14. What is fulminant Hepatitis?
- A severe and sudden form of Hepatitis that can lead to acute liver failure.
15.How long does it take to recover from Hepatitis A?
- Recovery typically takes 1–2 months, but it may take longer in some cases.
16. Does Hepatitis C always cause symptoms?
- No, many people with Hepatitis C are asymptomatic until significant liver damage has occurred.
17. How does alcohol affect Hepatitis?
- Alcohol accelerates liver damage in all forms of Hepatitis and should be avoided.
18. Can Hepatitis B or C lead to liver cancer?
- Yes, chronic infections with Hepatitis B or C are major risk factors for liver cancer.
19. Is Hepatitis A deadly?
- It is rarely fatal, but severe cases, particularly in older adults or those with pre-existing conditions, can lead to acute liver failure.
20. What global efforts are in place to eliminate Hepatitis?
- Initiatives like the World Health Organization’s Global Hepatitis Strategy aim to eliminate viral hepatitis as a public health threat by 2030.
Conclusion: Building Awareness and Empowering Prevention
Hepatitis A, B, and C each present unique challenges, but with early detection, vaccination, and effective treatment, their impact can be significantly reduced. Education, public health initiatives, and ongoing research are critical in combating the global burden of hepatitis. By prioritizing prevention and fostering a supportive environment for those affected, we can work towards a healthier future free of hepatitis-related complications.
Related video: