
Pneumonia is a serious infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. These air sacs may fill with fluid or pus, causing symptoms such as coughing, fever, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia can affect anyone, but it is particularly dangerous for infants, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is essential for effective management and prevention.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia is caused by various infectious agents, including:
- Bacteria:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae (most common cause of bacterial pneumonia).
- Haemophilus influenzae.
- Viruses:
- Influenza virus.
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
- SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19).
- Fungi:
- Pneumocystis jirovecii.
- Cryptococcus species.
- Other Causes:
- Aspiration pneumonia occurs when food, drink, or vomit is inhaled into the lungs.
- Chemical exposure can cause chemical pneumonia.
Indications of Pneumonia
Early indications of pneumonia may include:
- Persistent cough.
- Shortness of breath during simple activities.
- Chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing.
- High fever accompanied by chills.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Symptoms can vary based on the type of pneumonia and the individual’s overall health. Common symptoms include:
- Mild Symptoms:
- Fatigue.
- Dry cough.
- Mild fever.
- Severe Symptoms:
- Productive cough with yellow or green mucus.
- Rapid or shallow breathing.
- Confusion, especially in older adults.
- Bluish lips or fingernails (cyanosis).
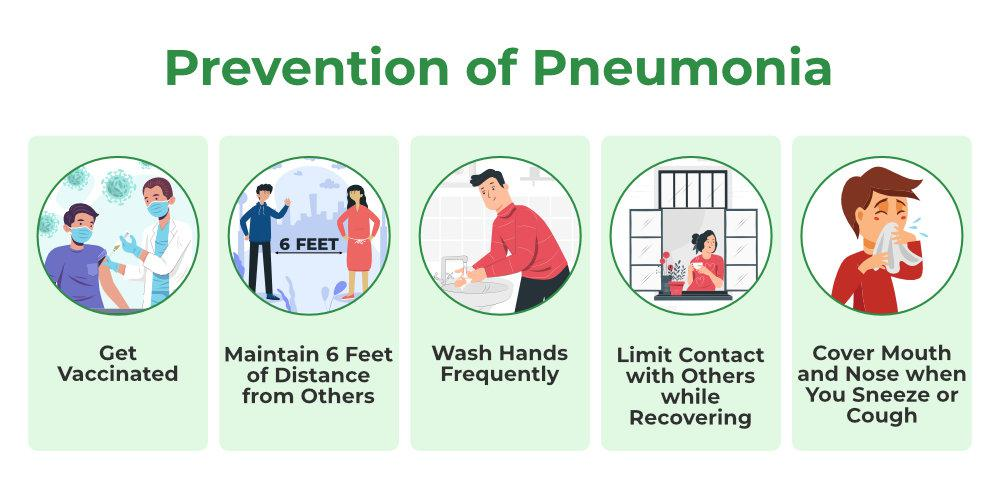
Prevention Strategies for Pneumonia
Preventing pneumonia involves a combination of vaccines, lifestyle changes, and hygiene practices:
- Vaccinations:
- Pneumococcal vaccine for children and older adults.
- Influenza vaccine to prevent flu-related pneumonia.
- Hygiene Practices:
- Regular handwashing with soap and water.
- Avoiding contact with sick individuals.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Quit smoking to reduce lung damage.
- Maintain a balanced diet and exercise regularly to boost immunity.
- Managing Chronic Conditions:
- Ensure proper treatment of conditions like asthma, diabetes, and heart disease.
Myths and Facts About Pneumonia

- Myth: Pneumonia is not contagious. Fact: While the condition itself is not contagious, the germs causing it can spread.
- Myth: Pneumonia only affects the elderly. Fact: Pneumonia can affect people of any age, though certain groups are at higher risk.
- Myth: Antibiotics can treat all types of pneumonia. Fact: Antibiotics are effective for bacterial pneumonia but not for viral or fungal pneumonia.
- Myth: Pneumonia always causes a high fever. Fact: Some types of pneumonia, especially in older adults, may not cause noticeable fever.
Treatments and Therapy
Medication-Based Treatments
- Antibiotics: For bacterial pneumonia (e.g., amoxicillin, azithromycin).
- Antivirals: For viral pneumonia caused by influenza or COVID-19.
- Antifungal Medications: For fungal pneumonia.
- Oxygen Therapy: To address low blood oxygen levels in severe cases.
Surgical Treatments
- Rarely needed but may include draining abscesses or repairing lung damage.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
- Breathing exercises and pulmonary rehabilitation can improve lung function post-recovery.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Interventions
- Rest and hydration to support recovery.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol during recovery to reduce lung strain.
Alternative and Complementary Medicine
- Herbal remedies like ginger or turmeric may alleviate symptoms but should complement, not replace, medical treatments.
Psychotherapy and Counseling
- Emotional support for individuals with prolonged recovery or post-pneumonia fatigue.
Immunizations and Vaccines
- Pneumococcal vaccines (PCV13 and PPSV23) and annual flu vaccines are highly recommended.
Stem Cell Therapy
- Experimental research explores the use of stem cells to repair lung damage.
Gene Therapy
- Emerging studies focus on genetic modifications to enhance lung defense against infections.
Top 20 FAQ on Pneumonia
1. What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs (alveoli) in one or both lungs, often causing them to fill with fluid or pus, leading to difficulty breathing.
2. What causes pneumonia?
Pneumonia can be caused by:
- Bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae).
- Viruses (e.g., influenza or respiratory syncytial virus).
- Fungi (e.g., Aspergillus or Histoplasma).
- Inhaled substances like toxic chemicals or food particles.
3. How is pneumonia diagnosed?
Pneumonia is diagnosed through:
- Chest X-rays: To detect fluid or inflammation in the lungs.
- Blood tests: To check for infections.
- Sputum analysis: To identify the microorganism causing the infection.
4. Can pneumonia be prevented?
Yes, prevention strategies include:
- Vaccines (e.g., pneumococcal and flu vaccines).
- Good hygiene, like regular handwashing.
- Avoiding smoking and staying active to strengthen the lungs.
5. Is pneumonia contagious?
The germs that cause pneumonia can be contagious, especially bacterial and viral forms. However, fungal pneumonia and aspiration pneumonia are not typically spread from person to person.
6. What are the risk factors for pneumonia?
- Being under 5 or over 65 years old.
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Chronic illnesses like asthma, diabetes, or heart disease.
- Weakened immune systems due to conditions like HIV or cancer.
7. What are the signs of severe pneumonia?
- High fever and chills.
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
- Chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing.
- Cyanosis (blue or gray lips, nails, or skin).
8. How long does pneumonia last?
Recovery time depends on the severity and type of pneumonia:
- Mild cases may improve in 1-2 weeks.
- Severe cases can take weeks to months for full recovery.
9. Can pneumonia recur?
Yes, pneumonia can recur, especially in individuals with chronic health conditions, weakened immunity, or those who smoke.
10. What’s the difference between bronchitis and pneumonia?
- Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, leading to cough and mucus.
- Pneumonia: Infection of the air sacs in the lungs, often more severe and accompanied by fever and difficulty breathing.
11. Do I need antibiotics for pneumonia?
Antibiotics are only effective for bacterial pneumonia. Viral pneumonia is treated with supportive care, and antifungal medications are used for fungal pneumonia.
12. Can pneumonia cause permanent damage?
In severe cases, pneumonia can lead to lung scarring (fibrosis) or long-term reduced lung function, especially if left untreated.
13. What should I eat while recovering?
- Foods rich in vitamins and minerals, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- High-protein foods like eggs and lean meat.
- Plenty of fluids, including water, herbal teas, and broths, to stay hydrated.
14. When should I see a doctor?
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent high fever.
- Shortness of breath or chest pain.
- Confusion, especially in older adults.
- Worsening symptoms despite home care.
15. Is pneumonia more dangerous for smokers?
Yes, smoking damages lung tissues and weakens the immune system, making smokers more susceptible to severe pneumonia.
16. What are the complications of pneumonia?
- Sepsis: A life-threatening response to infection.
- Lung abscesses: Pockets of pus in the lungs.
- Respiratory failure: When the lungs cannot supply enough oxygen to the body.
- Pleural effusion: Fluid buildup around the lungs.
17. Can children get pneumonia?
Yes, children, especially those under 5 years old, are at higher risk and may experience more severe symptoms.
18. How does age affect pneumonia severity?
Older adults often experience more severe cases of pneumonia due to weaker immune systems and the presence of chronic illnesses.
19. Are there long-term effects of pneumonia?
Some individuals may experience lingering fatigue, shortness of breath, or reduced lung capacity, particularly after severe or recurrent pneumonia.
20. What role does climate play in pneumonia?
Cold, damp weather can increase susceptibility to respiratory infections, but pneumonia itself is caused by infectious agents, not the climate.
Conclusion: Breathing Easier Through Awareness
Pneumonia is a serious yet preventable and treatable condition when addressed promptly. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, and adhering to preventive measures like vaccination and hygiene practices, we can significantly reduce its impact. Advances in medical research and therapeutic interventions continue to offer hope for better outcomes and quicker recoveries. Let us prioritize lung health and work together to combat pneumonia for a healthier, breath-filled future.
Related video: